Science News
& Faculty Articles
Unusual Seismic Phenomenon Heard Around the World

by

A “Mystery Signal” puzzles seismologists, as it was unprecedented in the records. In a National Geographic Article from 28th Nov. 2018 a couple of seismologic Experts discussed a global Phenomenon on 11th Nov 2018 just before 9:30(UT), that has emerged from the ancient African seismic activity zone at the Mayotte Islands located between Africa and the northern Tip of Madagascar. It was first discovered and posted on Twitter by an earthquake enthusiast with the handle @matarikipax, who was monitoring U.S. Geological Survey’s real-time seismogram displays.
I don’t think I’ve seen anything like it. […] Yet many features of the waves are remarkably weird—from their surprisingly monotone, low-frequency “ring” to their global spread [, …] researchers are still chasing down the geologic conundrum. – Göran Ekström, Professor of Earth and...
An Approach to Manipulate Small Objects with Light
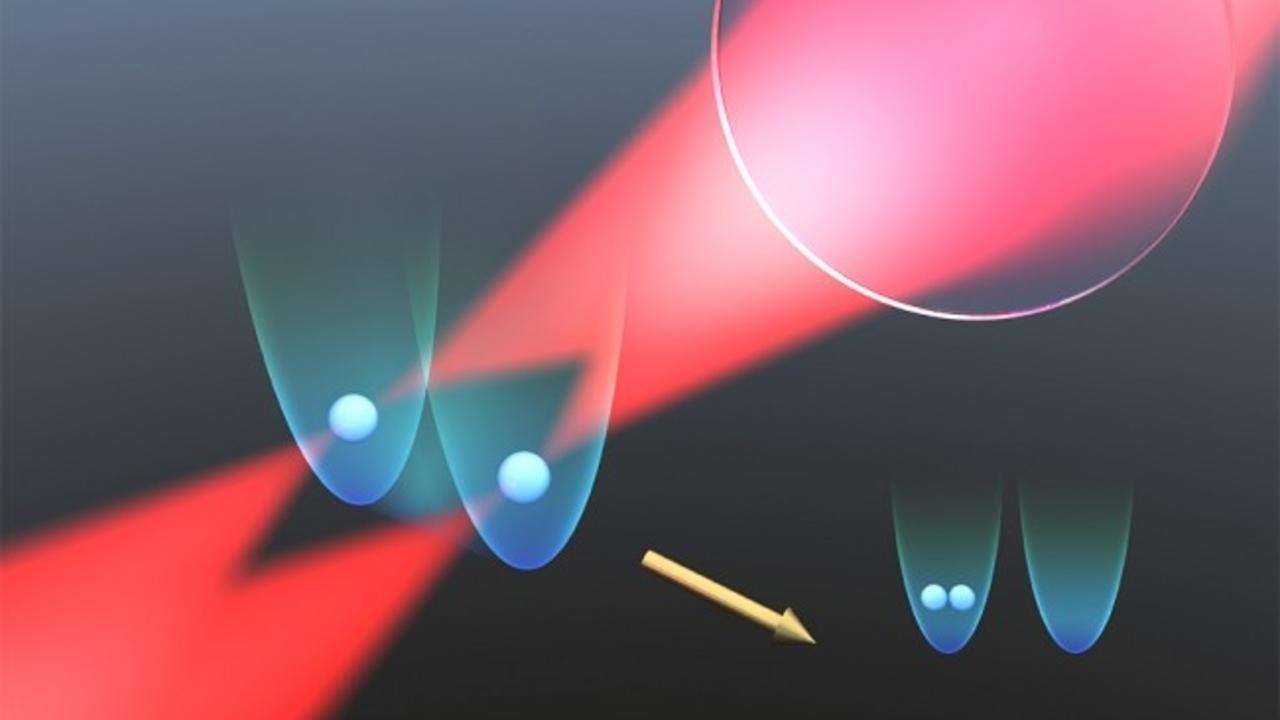
Article by Dr. Olivier Alirol, Resonance Science Foundation Research Scientist
Suspected from the outset Kepler’s observations of comet tails, the fact that light exerts forces on matter, and therefore on objects is now well established. Thanks to the work of Arthur Ashkin among many others, optical traps are now a reality. Using laser beams optical levitation of microspheres is used nowadays in many applications from stretching DNA to nanotechnology, spectroscopy, stochastic thermodynamics and critical Casimir forces.
Structuring light makes optical manipulation techniques possible, like using the Spatial Light Modulators (SLMs) to produce holographic optical traps (HOTs). These Spatial Light Modulators are liquid crystal technology with a fast and precise control of the beam shape used to control multiple particles in 2D and 3D configurations.
Previously holographic traps were limited to particular classes of light (scalar light), so it is very exciting that we can reveal a...
Music for the Heart

By Dr.
A recent publication indicates Yoga-Music at bedtime enhances the hearts variability in beat to beat distances. The heart is not only pumping, but pulsing with fractal fluctuations. The more flexible it is, the healthier you are. The pace will increase while breathing in and slow down during exhalation. The breath is giving a feedback to the nervous centers in the most archaic parts of the brainstem, the elongated spinal cord in the neck. It is responsible for the basic functions controlled by the unconscious nervous system. The variability of the heart can be entrained by coherent breathing techniques to a coherent beat-to-beat wave function or even a circular Poincaré-Plot. This state is called cardiac coherence and entrains the brain in its quite long refraction time of the pacemaker cells inside the “Gate to Consciousness” (Thalamus), which is why breathing techniques are used as a...
First Virtual Reality Simulation of a Supermassive Black Hole

Image from original paper: it depicts the virtual simulation of Sag. A* for an observer placed very close to it.
Article by: Dr. Inés Urdaneta, Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
As mentioned in a previous article, the Event Horizon Telescope is an international collaboration aiming to obtain the first real image of the event horizon (EH) of a black hole using a set of antennas scattered around the globe. EHT has been monitoring and collecting data from the supermassive Black Hole (SMBH) at the core of the Milky Way galaxy, known as Sagittarius A*, and results are expected very soon, probably 2019.
Now, for the first time, the virtual reality simulation of Sagittarius A* has been achieved by a group of scientists at Radbound University and collaborators from the Institute of theoretical Physics, in Germany, and the Mullard Space Science laboratory, at the University College London. In their article “Observing Supermassive Black Holes in virtual...
From the Planck Constant to the Kilogram

Article by Dr. Olivier Alirol, RSF Research Scientist
The year 2018 is historic for the world of measurement. It will mark the redefinition of the International System (SI), and more particularly of four of its units: the kilogram, the ampere, the kelvin and the mole. In November 2018, the 26th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) will vote on the new definitions of these units. These should be established on the basis of fundamental physical constants. LNE, the French metrology pilot, is actively contributing to the redesign of SI, in particular through the redefinitions of the kilogram, ampere and kelvin.
The International System of Units (SI) consists of a set of internationally recognized basic units controlled by the Comité International des Poids et Mesures (CIPM).
Today, the IS has 7 units that can be found in all aspects of our daily lives, let alone in the industry:
- Kilogram (Planck Constant, speed of light, time)
- Meter (time and speed of light)
- Second...
A Virtual Telescope the Size of the Earth!

By Dr. Inés Urdaneta / Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
Up to 2016, the biggest telescopes were composed of an array of antennas located in a particular site, like the one at Atacama Desert, in Chile. called ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter/ Submillimeter Array). Its construction dates from 2004 and consists of sixty-six 8-to-12-meter diameter antennas aiming to receive millimeter wavelengths. Among others things, ALMA is capable of performing deep space detections, what allows to obtain information about the first stars and galaxies that emerged billions of years ago at huge distances from us. Due to the universe expansion, most of these objects’ emissions have stretched out to the millimeter and submillimeter wavelengths.
Using a technique known as interferometry – or interference pattern between the signals received by each antenna, to recompose a complete unique image- the 66 antennas at ALMA work together as though they were a single...
Electromics – The Double-Aspect of Life

Article by
Biologist Dr. Daniel Fels recently published an essay in Biology on the interaction of matter and the so-called bioelectricity as a functional unity for regulation of living cells. The editor of the scientific textbook “Fields of the Cell” summarizes evidence of bioelectricity. He discusses interactions of internal bioelectricity with internal biochemical structures, as well as the sensitivity of Biosystems to external physical factors.
Fels explains “bioelectricity is generated by electrical charges of ions and molecules in an aqueous environment. Ions and oscillations of charged molecules as well as chemical reactions lead to electrical currents and electrostatic and electrodynamic fields.” This is very basic in biological systems and differs from the bio-photon discussion. Every heartbeat, nervous excitation or muscle contraction is physiologically...
A Two Layers Graphene Superconductor Material

Article by Dr. Olivier Alirol, Physicist, Resonance Science Foundation Research Scientist
Scientists have discovered that a two graphene layers can conduct electrons showing superconductivity if the two hexagonal nets are twisted against each other at a 1.1 degree angle. This finding could lead to room-temperature superconductors, a hypothetical material exhibiting superconductivity at temperatures above 0 °C (273.15 K). Most superconductors work only at temperatures close to absolute zero. Even ‘high-temperature’ superconductors are working in reality at −140 ºC. A material that displayed the property at room temperature — eliminating the need for expensive cooling — could revolutionize energy transmission, medical scanners and transport.
Increasing the temperature at which superconductivity occurs could have phenomenal technological applications
A current that could flow forever without losing any energy means transmission of power...
13.5-Billion-Year-Old Star Sheds Light On Star Formation

Article by Dr. Amira Val Baker, Astrophysicist, Resonance Science Foundation Research Scientist
A star that formed at the time of the early universe has just been identified, and its unique characteristics may reveal new insights to star formation.
Stars are theorized to have formed in the collapsing dust of a nebulae, with the star forming in the centre of rotation and the planets forming in the corresponding protostellar disk. It has also been hypothesized that low-mass stars and brown dwarfs could also be formed from gravitational instabilities in the extended protostellar disc. Computer simulations to explore this idea suggest such a possibility. However, as yet they have been unable to run the simulations long enough to verify that the fragments would survive disk migration. Now the discovery of a very old star may just be able to prove that they would survive.
In a paper recently published in the Astrophysical Journal, a team led by Kevin Schlaufman report the discovery of a...
Bioreactor Device Helps Frogs Regenerate Their Legs

Article by William Brown, Biophysicist, Resonance Science Foundation Research Scientist
A team of scientists designed a device that can induce partial hindlimb regeneration in adult aquatic African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis) by “kick-starting” tissue repair at the amputation site. Their findings, appearing November 6 in the journal Cell Reports, introduce a new model for testing “electroceuticals,” or cell-stimulating therapies.
“At best, adult frogs normally grow back only a featureless, thin, cartilaginous spike,” says senior author Michael Levin, developmental biologist at the Allen Discovery Center at Tufts University. “Our procedure induced a regenerative response they normally never have, which resulted in bigger, more structured appendages. The bioreactor device triggered very complex downstream outcomes that bioengineers cannot yet micromanage directly.”
The scientists 3-D printed the bioreactor...



